Conduct market research
Gather market intelligence across emergent technology domains and iteratively refine insights to manage uncertainty.

Buying that is open to innovation seeks innovative solutions by approaching the market with an outcome focus or challenge statement.
This means the end solution is unclear, making market research tougher for buying teams. Some technology domains are still emerging, and it’s uncertain which buying categories may contain the best solution. As a result, buying teams may struggle to gather enough insights for their market approach or procurement strategy.
Developing an outcome focus or challenge statement is a useful way to guide early research and align your buying team’s priorities.
Key definitions
Market research: the action or activity of gathering information about suppliers and solutions.
Market intelligence: information collected through market research.
Market insights: actionable understandings of a market, derived from data analysis, that inform strategic decisions and guide a market approach.
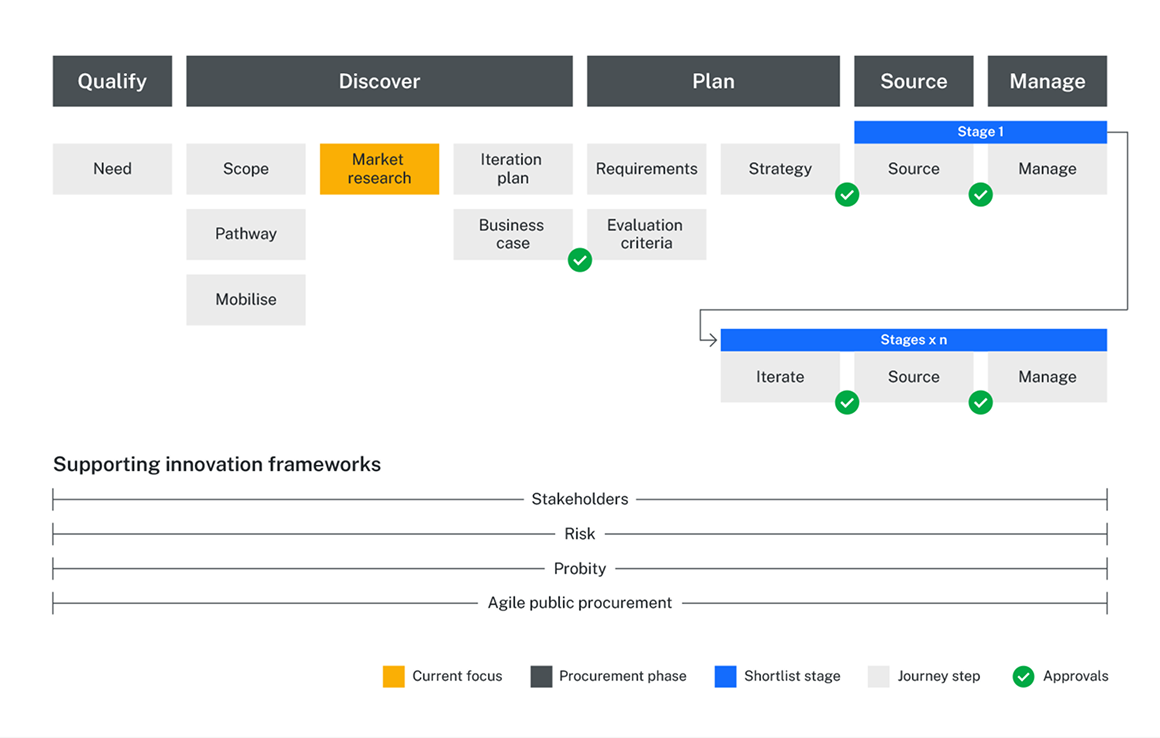
This page provides an overview of market research for outcome-focused innovation procurement. It shows how gathering market intelligence upfront and refining insights during buying stages can lead to better innovation results.
Buying teams will learn about:
- when to conduct market research
- which subject-matter experts (SMEs) to involve
- the scope of market research and its insights
- the risks of assuming solutions without adequate market insights
- sources of market intelligence and their strengths and weaknesses
- constraints in sharing market intelligence with buying projects or agencies
- the importance of refining market insights iteratively.
When to conduct market research
Understanding the market for an innovative technology solution is not a one-step process. It is iterative and often begins before a project starts. This process continues throughout procurement activities and into business operations after project delivery.
It starts with gathering market insights from various internal and external sources. These are then refined through the buying project as solutions are evaluated.
The biggest market research effort happens in the Discovery phase, after the scope is clear and before there is an approved business case or project mandate. However there are elements of market research at other points of the buyer journey, including:
- as an ongoing activity by ICT and digital strategy professionals and category sourcing experts
- during the Scoping step to inform problem shaping or challenge definition
- in the Plan phase to shape the procurement strategy
- in the Source phase, during evaluation of proposals
- during each testing stage, including business acceptance testing and evaluation of outcomes
- during regular business activities, where ICT and business teams collect feedback.
Who to involve
Including a range of expertise in the discovery phase helps develop a strong understanding of the market. Effective engagement with expertise is even more crucial when the solution is unclear, emerging technology could solve the problem or multiple solutions exist. The core buying team and experts should collaborate, share insights and form a comprehensive view of the market.
Effective engagement means:
- engaging experts before scope is locked in
- identifying relevant experts and their contributions by defining roles and responsibilities such as a RACI matrix, governance structure and stakeholder influence and engagement map
- inviting key experts to the project mobilisation
- considering whether any external subject-matter experts or resources may be needed to supplement internal experts
- collaborating on market research data and activities, as well as on analysis of information to drive relevant insights and consensus on implications for the project.
Not engaging experts in market research creates risks. Working in isolation can prevent experts from sharing their knowledge, leading to weaker insights and poor project design. Possible impacts include:
- knowledge gaps or wrong assumptions about solutions
- team confusion, conflict, or rework, causing project delays
- misaligned expectations about suppliers and solutions
- too many, too few, or low-quality supplier submissions
- increased chance of changes in procurement strategy due to unexpected developments leading to delays, which may include:
- adding or removing testing stages
- refining requirements
- adjusting evaluation criteria.
If changes stray too far from the initial market approach, the buying team may need to abandon the procurement and restart with a new market approach.
Stakeholders who help conduct market research
Expand the headings below to learn which stakeholders to engage and how they contribute in the Market research step:
Buying teams should work with the relevant ICT/digital product and technical domain leads to ensure strategic alignment before engaging the market, to understand:
- whether problem has already been solved elsewhere in NSW Government
- in-flight or planned projects seeking to solve the same problem
- whether the problem is worth solving and aligned to NSW Government strategic priorities
- existing supplier capability within NSW Government that can be expanded to support new use cases
- regulatory technology (RegTech) domain ethical risks and mitigants.
Buying teams should engage cyber security, data and privacy risk specialists during the discovery phase to form a hypothesis of the sorts of solutions that might be proposed and the risks that should be planned for. These experts deeply understand their own risk domains and can guide market research activities to understand the risk profile of potential solutions in advance (where the information is available).
During the Plan phase, these experts can:
- support risk identification and management in their respective technical domains
- help design testing stages as part of a multi-stage procurement strategy, to systematically identify risks and break them down into manageable chunks
- contribute to outcome-focused requirements and evaluation criteria for the market approach
- for multi-stage procurement approaches, contribute to increasingly technical requirements for testing stages
- possibly be appointed to the evaluation committee for expert assessment of their risk domain.
During the Source phase/s, they may evaluate supplier solutions and capability against criteria. They may also help refine market insights and adjust future testing stages to manage emerging risks and reflect other new insights.
Enterprise architects, ICT business partners and relevant technical domain specialists can supplement strategic alignment (see ICT strategy professional box). This helps refine the hypothesis about solutions that might be put forward. More specifically, they can advise on:
- which other technical experts should be engaged in the buying project
- known solutions in the market, pros and cons
- outcomes of previous approaches to market
- Domain-specific matters including any associated requirements (e.g. artificial intelligence ethics policy and assurance framework)
- existing supplier capability within NSW Government that can be expanded to support new use cases
- in-flight or planned projects seeking to solve the same problem
- ICT domain ethical risks and mitigants
- testing stages that could be part of an innovation buying pathway
- options to outsource ICT market scanning or market curation.
During the Plan phase, these experts can:
- support risk identification and management
- help design testing stages as part of a multi-stage procurement strategy, to systematically identify risks and break them down into manageable chunks
Buying teams should engage procurement specialists with ICT category and sourcing expertise during the Discover phase to ensure strategic alignment and help form a hypothesis about solutions the market might put forward. They can advise on:
- which ICT categories or supplier capabilities might be relevant
- market insights through their procurement experience with ICT suppliers
- procurement-related risks and mitigants for the ICT procurement category
- known suppliers and solutions, pros and cons
- outcomes of previous approaches to market
- existing solutions within NSW Government that can be expanded to support new use case sources of external market intelligence
- procurement pipelines or live sourcing activity that could be related to the project
- procurement resources that may be needed to support a multi-stage approach, including the potential for additional probity support.
During the Plan phase, they should:
- contribute to the risk assessment, with a focus on procurement and probity risks
- help design testing stages as part of a multi-stage procurement strategy, to ensure appropriate policy compliance, governance and probity
- review outcome-focused requirements and evaluation criteria for the market approach
- for multi-stage procurement approaches, review increasingly technical requirements for testing stages
- possibly be appointed to the evaluation committee for oversight of policy compliance, consistency with evaluation plans and probity.
During the Source phase/s, they may evaluate supplier solutions and capability against criteria. They may also help refine market insights and adjust future testing stages to manage emerging risks and reflect other new insights.
Buying teams should engage legal experts as soon as the agency’s legal team is willing.
During the Plan phase, if a multi-stage approach is being adopted, they should be briefed on the approach and can advise on suitable contracting arrangements to manage contractual risks for each stage and the overall project. They can also advise on the most suitable instruments to support a market approach and the terms and conditions that might need to be considered for testing and final implementation stages.
During the Source phase(s), they will review and contribute to tender documentation and help prepare and negotiate contracts. Legal experts may bring direct experience from previous negotiations with the same or similar suppliers.
Buying teams should engage service design professionals during the Discover phase to help align the buying team and formulate a hypothesis about which solutions the market might propose. They may be able to advise on several of the following:
- methods to mobilise and align a buying team and experts
- engagement of end users and other key stakeholders to understand the current and desired state
- synthesis and prioritisation of insights
- defining the problem to be solved
- framing a challenge statement the market can respond to
- value analysis that defines the impact of the problem, and the value to users and the business of solving it
- methods for early market engagement
- facilitation and co-design for engagements
- solution possibilities and hypothesis on market proposals
- market intelligence research.
During the Plan phase, they should:
- contribute to the risk assessment, with a focus on solution fit and value
- help design testing stages as part of a multi-stage procurement strategy, to build confidence in solution fit and supplier capability
- contribute to outcome-focused requirements and evaluation criteria for the market approach
- for multi-stage procurement approaches, help retain a link between increasingly technical requirements for testing stages and the challenge to be solved
- possibly be appointed to the Evaluation Committee for expert assessment of the solution fit.
During the Source phase(s), they may design and facilitate showcases, supplier briefings and buying guides. They may evaluate supplier solutions and capability against criteria. They may also help refine market insights and adjust future testing stages to manage emerging risks and reflect other new insights.
Buyers should engage owners of operational business functions and related technology, as well as end users during the Discover phase to build an understanding of the problem space. They may provide advice or contribute to:
- identifying who should contribute to market research
- shaping the problem to be solved, including current state insights
- determining the value and priority of a potential solution
- solutions they have considered or their hypothesis of solutions the market might put forward
- framing of the challenge and defining requirements
- previous research undertaken and insights gained
- previous engagement undertaken such as market sounding or briefings.
During the Plan phase, they may:
- have input to the design of testing stages as part of a multi-stage procurement strategy, to ensure testing reflects the business environment, end user perspectives, relevant data and business processes
- contribute to outcome-focused requirements and evaluation criteria for the market approach
- for multi-stage procurement approaches, contribute to increasingly technical requirements for testing stages with a focus on business processes, end users and data types, potentially ensuring the availability of people and data for testing
- possibly be appointed to the evaluation committee for assess usability, functionality and user experience.
During the Source phase(s), they may evaluate supplier solutions and capability against criteria. They may attend or participate in showcases and supplier briefings.
Buying teams should seek probity advice as early as possible, so that if a probity advisor is recommended, they have an opportunity to understand the buying project objectives and provide guidance and/or advice before governance decisions are made.
During the Discover phase they may provide advice on early market engagement activities.
During the Plan phase, they may provide advice on, and contribute to the risk assessment and probity plan. In a multi-stage procurement they may be asked to provide advice on probity arrangements for the initial proposal stage and transitions into subsequent testing and/or implementation stages.
During the Source phase(s), they will provide advice on supplier engagement activities, evaluation and communications.
Market research resources
Support accurate and confident decision-making in the procurement process.
Iteratively gather insight to reduce risk, increase confidence and combat uncertainty.
Evaluate all the sources of market intelligence and what can be shared.