Document your market approach
Document how your market approach will achieve buying objectives and comply with NSW Government procurement policies.

Before approaching the market, buying teams usually need to demonstrate how their market approach will achieve buying objectives and comply with NSW Government procurement policies. This may include an approval step before teams can approach the market.
While specific approval steps and processes vary between agencies, buying teams usually need some level of documentation that explains and justifies their market approach.
We refer to the central document in this process as an innovation buying strategy. Agencies may also call this a procurement plan, complex procurement plan, procurement strategy or sourcing strategy.
Agencies may require other documents to support an innovation buying strategy. These may include a covering briefing note, a statement of requirements and a risk assessment.
An innovation buying strategy and any supporting documentation draws from the insights and decisions of all the preceding steps in the Discovery and Plan phases.
Read more about how to build the innovation buying strategy.
For outcome-focused, multi-stage procurement, buying teams should also consider creating innovation challenge guidelines at this step. Preparing this market-facing document before it is needed is advantageous. It can:
- be a single source of truth for the team
- ensure the market approach is designed and communicated with the audience in mind (i.e. suppliers)
- speed up the preparation of market-facing documentation
- support effective briefing of approvers.
Read more about innovation challenge guidelines.
When to document your market approach
Documenting the market approach is the last step in the Plan phase of procurement. Approval of the innovation buying strategy signals the end of the Plan phase.
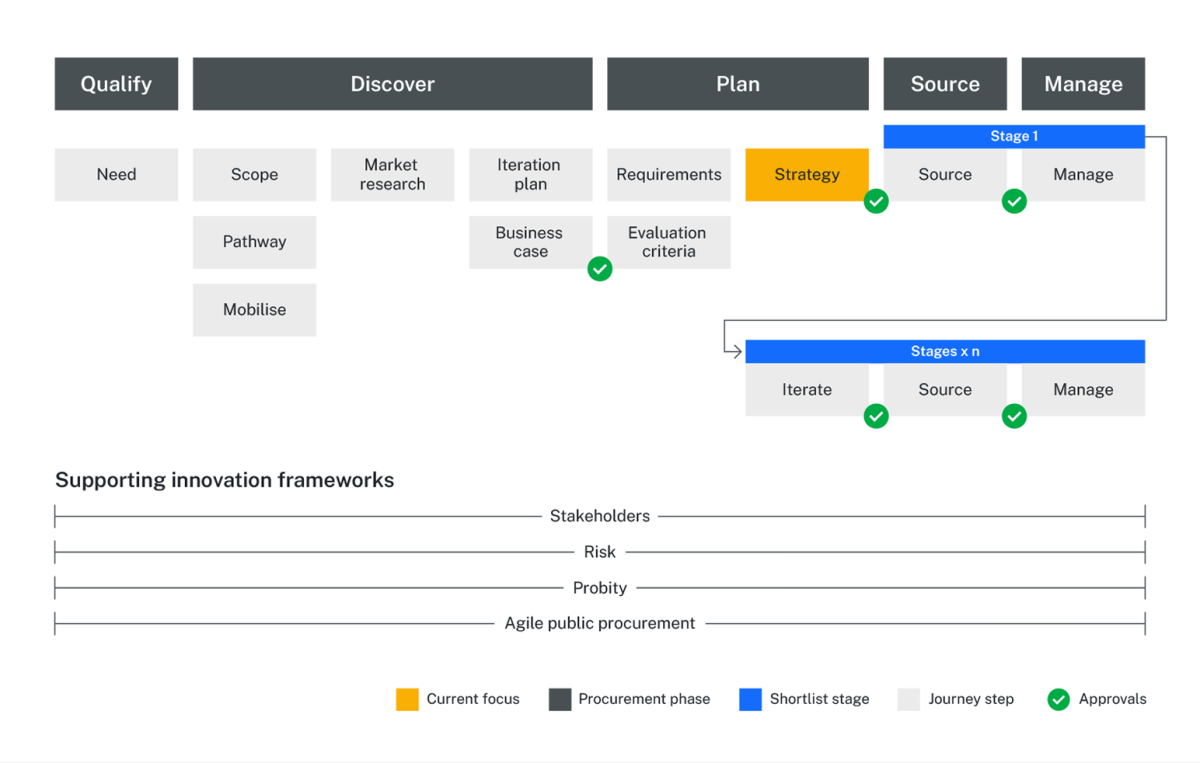
Who to involve and why
Buying teams need to bring together several different areas of expertise to shape and capture the market approach. This diversity ensures the strategy will achieve buying objectives and is accurately communicated to decision-makers. Missing market expertise can result in:
- knowledge gaps about objectives or procurement options may cause down-stream issues
- incorrect assumptions about, or misinterpretations of, the procurement processes
- too much detail locked in early, or too little detail considered
- too many, too few or low quality supplier submissions
- higher likelihood of changes to the procurement strategy, potentially causing a significant departure from the original documented market approach (requiring the process to be abandoned and restarted).
Active collaboration between the core buying team and the experts listed below will make the most of their combined knowledge and experience. This means working out loud or workshopping the strategy together, rather than working separately on individual sections.
Working this way results in sharing of different perspectives, creates new insights and improves buy-in to the project.
Expand the types of experts below to learn how each can contribute to documenting a market approach.
Buying teams should work with the relevant ICT/digital product, technical domain, cyber security, data and privacy risk specialists to ensure the market approach will achieve buying objectives and comply with NSW Government ICT policies.
These experts can assist with:
- outcome-focused requirements, technical constraints and evaluation criteria for the market approach
- data and insights from previous approaches to market
- interpretation of market research and implications for the market approach
- ICT risk identification and management
- describing the testing stages that form part of an innovation buying pathway.
Buying teams should engage procurement specialists with ICT category and sourcing expertise when documenting the market approach to help reach the right suppliers.
They can advise on:
- which ICT categories or supplier capabilities might be relevant
- outcomes of previous approaches to market
- procurement-related risks and mitigants for the ICT procurement category
- procurement resources that may be needed to support a multi-stage approach, including the potential for additional probity support
- compliance with procurement policies.
Buying teams should consult with legal expertise on suitable instruments to support a market approach and the terms and conditions that might need to be considered for testing and final implementation stages. Terms and conditions will be more formally documented in the market-facing documents in the Source phase, however some key terms may need to be highlighted for decision-makers as part of the buying strategy.
Buying teams should engage service design specialists while documenting the market approach and writing innovation challenge guidelines. Service designers help align the buying team, synthesise insights and facilitate collaboration sessions.
Buyers can engage owners of operational business functions and related operational technology, as well as end users, to ensure the buying strategy accurately captures:
- problem to be solved, including the current state
- the challenge and defining requirements
- previous industry engagement undertaken such as market sounding or briefings
- linkages between the business environment, end user perspectives, relevant data and business processes on the one hand, with outcome-focused requirements and evaluation criteria on the other.
Buying teams should seek probity advice as early as possible. This way, if a probity advisor is recommended, they have an opportunity to understand the buying project objectives and provide guidance before significant decisions are made.
During the Plan phase they may provide advice on, and contribute to, the risk assessment and probity plan. In a multi-stage procurement they may be asked to provide advice on probity arrangements for the initial proposal stage and transitions into and between subsequent testing and/or implementation stages. This advice and any planned actions resulting from it should be captured in a buying strategy.
Expect and manage change
Buying innovation requires an agile, iterative approach to procurement - one that adapts to new information. Buying teams that are not able to iterate may not be managing risk effectively. Revisiting assumptions and decisions in light of new evidence is a great sign that innovation is occurring and that uncertainty is being managed well.
Read more about agile procurement and iteration plans.
For a buying strategy to support an agile approach to procurement, it needs to be set up to iterate. It should define multiple distinct stages, with gates between each. Gates are an opportunity to revisit the parts of the strategy that have not been executed. This is in contrast to the standard approach to buying strategies which have a single stage that, once approved, often seems set in stone.
An innovation buying strategy should prepare approvers for potential iteration by explaining:
- that they should expect changes to the buying strategy
- how changes will be justified by evidence
- which changes are likely based on current evidence or levels of confidence
- how changes will be managed, approved (if necessary) and communicated.
Read more about how to set up for effective iteration and change management within an innovation buying strategy.
Document your market approach resources
Adapt buying strategy templates for uncertainty and complexity
Work with uncertainty in buying categories and contract templates.
Concisely communicate key sections of the tender documents in plain English